Robots Gain 3D Vision with New GeoVLA Framework
Robots Finally See the World Like We Do

Imagine trying to navigate your kitchen blindfolded - that's essentially how today's robots experience the world. While artificial intelligence has made tremendous strides, most robotic vision systems still struggle with basic spatial awareness. Current vision-language-action (VLA) models like OpenVLA and RT-2 rely on flat, two-dimensional images, leaving them literally blind to depth and positioning.
This limitation becomes painfully obvious in unstructured environments where depth perception matters. Picture a robot arm trying to grab a cup on a crowded table - without understanding which objects are closer or farther away, simple tasks become frustrating exercises in trial and error.
A Three-Dimensional Breakthrough
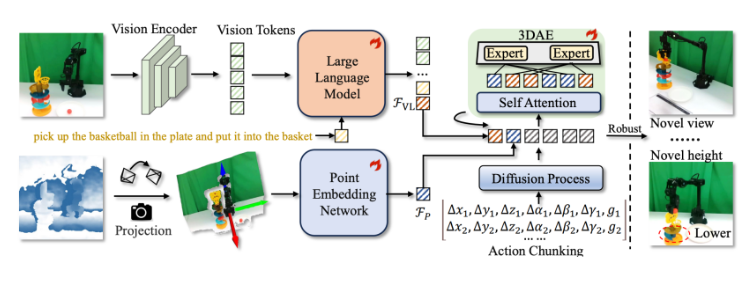
The research team at Yueli Lingji has developed what might be the glasses robots desperately need. Their GeoVLA framework introduces true 3D perception by combining two innovative components:
- Point Cloud Embedding Network (PEN): Processes spatial data much like our brain interprets depth cues
- Spatial-Aware Action Expert (3DAE): Translates that spatial understanding into precise movements
"We've essentially given robots their missing dimension," explains Dr. Lin Sun, lead researcher on the project. "Where current systems see flat pictures, GeoVLA builds mental models of space - understanding not just what objects are, but where they actually exist in three dimensions."
Putting Depth Perception to the Test
The results speak volumes about this new approach:
- 97.7% success rate on LIBERO benchmark tests (outperforming previous models)
- Exceptional handling of complex objects in ManiSkill2 simulations
- Remarkable adaptability to unexpected scenarios and perspective changes
The secret lies in GeoVLA's task separation approach: traditional visual-language models handle object identification while specialized components manage spatial reasoning and movement planning.
What This Means for Robotics
The implications extend far beyond laboratory demonstrations:
- More reliable manufacturing robots that can handle irregular parts
- Household assistants capable of navigating cluttered spaces safely
- Search-and-rescue bots that better understand collapsed structures
The team has made their work publicly available, inviting further development from the robotics community.
Key Points:
- Problem: Current robot vision lacks depth perception
- Solution: GeoVLA adds true 3D understanding through dual-stream architecture
- Components: PEN for spatial mapping + 3DAE for movement planning
- Results: Near-perfect performance in controlled tests with strong real-world potential
- Availability: Framework accessible via project website




